Master AI development with practical implementation strategies, code optimization, and best practices for scalable AI solutions.
How 120B Parameters Still Start from One Simple Neural Network Flow
Read Time: 6 minutes | Last Updated: January 2025
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Myth of Complexity
- The Simple Foundation
- Breaking Down the Core Flow
- From Simple to Scale: The Real Challenge
- Why This Matters for Students
- The Engineering Marvel
- Conclusion
Introduction
I always hear "70B parameters," "120B parameters," "state-of-the-art LLMs," and it sounds almost mythical. Today something clicked for me.
We always hear phrases like "70B parameters," "120B parameters," "state-of-the-art LLMs," and it sounds almost mythical. But when you zoom in, the core idea is surprisingly simple.
It's just a flow of basic operations—the same foundation that powers every neural network, from a simple 10-neuron model to a massive 120B-parameter language model.
This post breaks down that fundamental flow and shows how something so simple at the micro level becomes so powerful at scale.
The Myth of Complexity
The math isn't as scary as people make it sound. The fundamentals are not complicated. But turning those fundamentals into a frontier-level LLM? That's where the real complexity begins.
The Simple Foundation
Every large model starts with this exact flow:
Input → Weights → Linear Combination → Activation → Loss → Gradients → UpdateThat is the exact foundation behind every "billion-parameter" model.
The Core Flow Breakdown:
Input | Weights | Linear Combination
Z = wx + b| Activation
a = sigmoid(z)| Loss (Binary Cross Entropy)
-y log(a) + (1-y) log(1-a)| Gradients
∂L/∂w, ∂L/∂b| Update Gradients
w = w - learning_rate * ∂L/∂w
b = b - learning_rate * ∂L/∂bThat's it. That's the foundation.
Flow Diagram
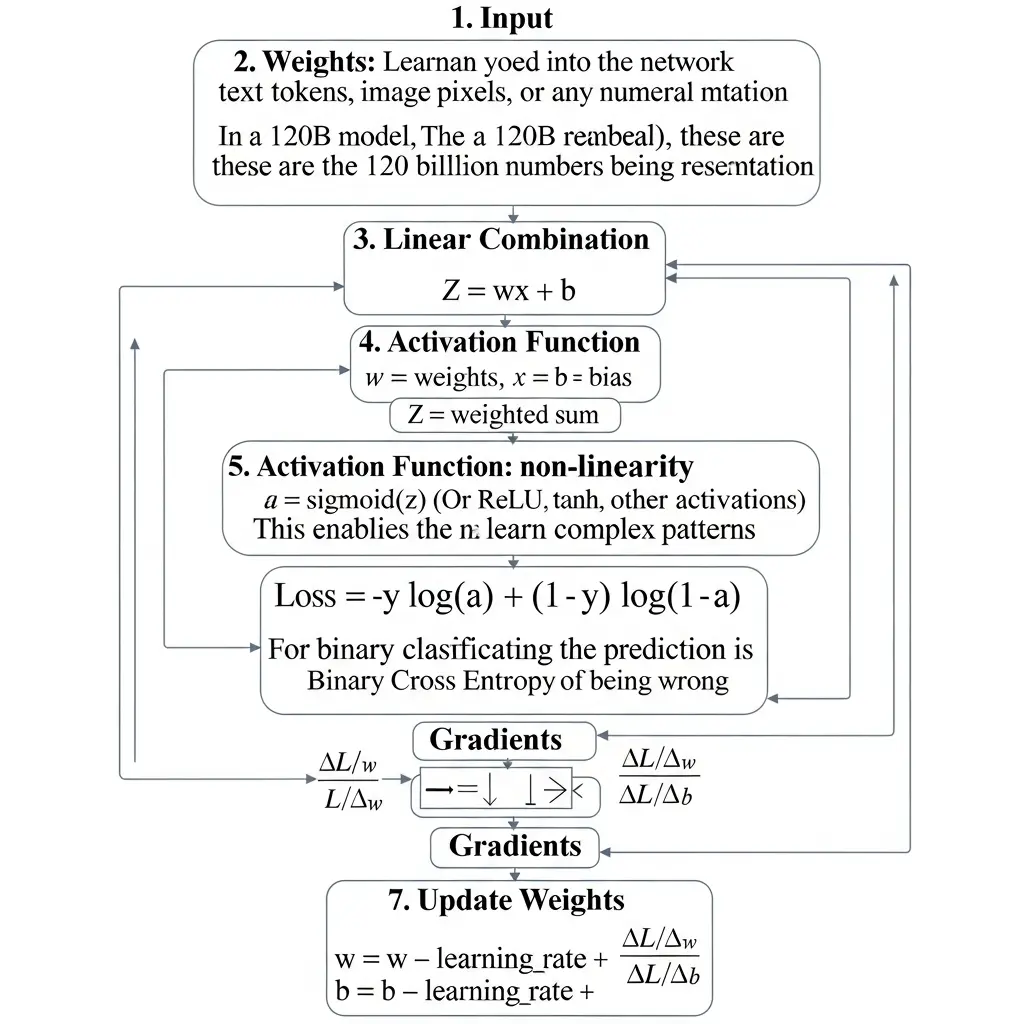 The complete neural network flow: From input through weights, linear combination, activation, loss calculation, gradients, and weight updates—the foundation of every AI model.
The complete neural network flow: From input through weights, linear combination, activation, loss calculation, gradients, and weight updates—the foundation of every AI model.
From Simple to Scale: The Real Challenge
Scaling this flow to 120B parameters is where complexity grows:
The Scaling Challenge
At the micro level:
- One neuron: simple math
- One layer: manageable
- One forward pass: straightforward
At 120B parameters:
- 120 billion weights to optimize
- Thousands of layers
- Distributed across hundreds of GPUs
- Months of training time
- Millions of dollars in compute
What Makes It Complex
-
Distributed Training
-
Splitting the model across multiple GPUs
- Synchronizing gradients across nodes
-
Handling communication bottlenecks
-
Memory Management
-
Fitting 120B parameters in memory
- Gradient checkpointing
-
Mixed precision training
-
Optimization Tricks
-
Learning rate schedules
- Advanced optimizers (Adam, AdamW)
- Gradient clipping
-
Weight initialization strategies
-
Hardware Requirements
-
Thousands of GPUs working in parallel
- Specialized infrastructure
-
Power consumption measured in megawatts
-
Engineering Challenges
- Fault tolerance
- Data pipeline optimization
- Model parallelism strategies
- Debugging at scale
Why This Matters for Students
If you're learning:
The Fundamentals Are Not Complicated
- The core math is accessible
- Start with one neuron
- Build up layer by layer
- Understand the flow before scaling
The Complexity Is in the Engineering
- Scaling requires systems knowledge
- Distributed computing expertise
- Optimization techniques
- Infrastructure management
The Learning Path
- Master the fundamentals (this flow)
- Build small networks (1-10 layers)
- Understand optimization (gradient descent variants)
- Learn distributed systems
- Study large-scale training techniques
The Engineering Marvel
What makes modern LLMs impressive isn't just the math—it's the engineering:
- Efficiency: Training a 120B model in months instead of years
- Reliability: Keeping thousands of GPUs running for weeks
- Optimization: Techniques that make training feasible
- Innovation: New architectures and training methods
The math is simple. The engineering is not.
Real-World Perspective
What You Can Build Today
With the fundamentals, you can:
- Build neural networks from scratch
- Understand how LLMs work internally
- Implement your own training loops
- Experiment with architectures
What Requires Scale
To train a 120B model, you need:
- $10-100M in compute resources
- Teams of engineers
- Months of development
- Specialized infrastructure
But you can understand how it works with just the fundamentals.
The Beautiful Simplicity
There's something elegant about this:
At the core: Simple mathematical operations
At scale: Systems that can understand language, generate code, and reason about complex problems
The same Z = wx + b that fits in a single line of code becomes the foundation for models that can:
- Write code
- Answer questions
- Generate creative content
- Solve complex problems
Conclusion
The fundamentals are not complicated. The core flow—input, weights, linear combination, activation, loss, gradients, update—is the same whether you're building a 10-neuron network or a 120B-parameter model.
The complexity comes from scaling: distributed training, memory management, optimization, and infrastructure. Understanding the fundamentals gives you the foundation to appreciate and work with large models.
Key Takeaways
- The math behind neural networks is accessible
- Every large model uses the same fundamental operations
- The challenge is in scaling, not the core concepts
- Start with fundamentals, then explore scaling techniques
- Engineering makes the difference at scale
For Students Starting Out
Don't be intimidated by "120B parameters." Start with one neuron, understand the flow, build small networks, and gradually explore larger systems. The fundamentals are your foundation—master them first, then tackle the engineering challenges of scale.
The journey from Z = wx + b to a 120B-parameter model is one of the most fascinating stories in modern AI. And it all starts with understanding that simple flow.
I'm learning the basics slowly and deliberately, and honestly… it's fascinating to see how something so "simple" at the micro level becomes so powerful at scale.
Interested in diving deeper into neural network fundamentals? Check out our guides on Advanced RAG Techniques and Traditional AI vs Generative AI Architectures to see how these fundamentals power modern AI systems.
Tags: #NeuralNetworks #DeepLearning #MachineLearning #LLM #AIEducation #Fundamentals #120BParameters #NeuralNetworkBasics #AILearning #DeepLearningFundamentals
Need Help Implementing AI Solutions?
I specialize in RAG systems, AI agents, and custom integrations. Let's build something extraordinary.
Get Expert Consultation
