Build advanced RAG systems with document retrieval and AI generation. Covers implementation strategies, code examples, and real-world applications.
Advanced RAG Techniques: From Basic to Smart AI Systems (2025)
Read Time: 8 minutes | Last Updated: January 2025
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Basic RAG?
- The Problems with Basic RAG
- What Makes RAG "Advanced"?
- Advanced RAG Architecture
- Key Components Explained
- Real-World Example
- Why LangChain, LlamaIndex & LangGraph Are the Best RAG Frameworks in 2025
- Implementation Benefits
- Use Cases for Advanced RAG
- Getting Started
- Conclusion
Introduction
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) has changed how AI systems work with information. But while basic RAG gets the job done, advanced RAG takes it to the next level. In this post, I'll show you the difference between basic and advanced RAG, and how modern tools like LangChain and LangGraph make building smart AI systems much easier.
What is Basic RAG?
Basic RAG is simple: when you ask a question, the system searches for relevant information and generates an answer. Think of it like a smart search engine that can write responses.
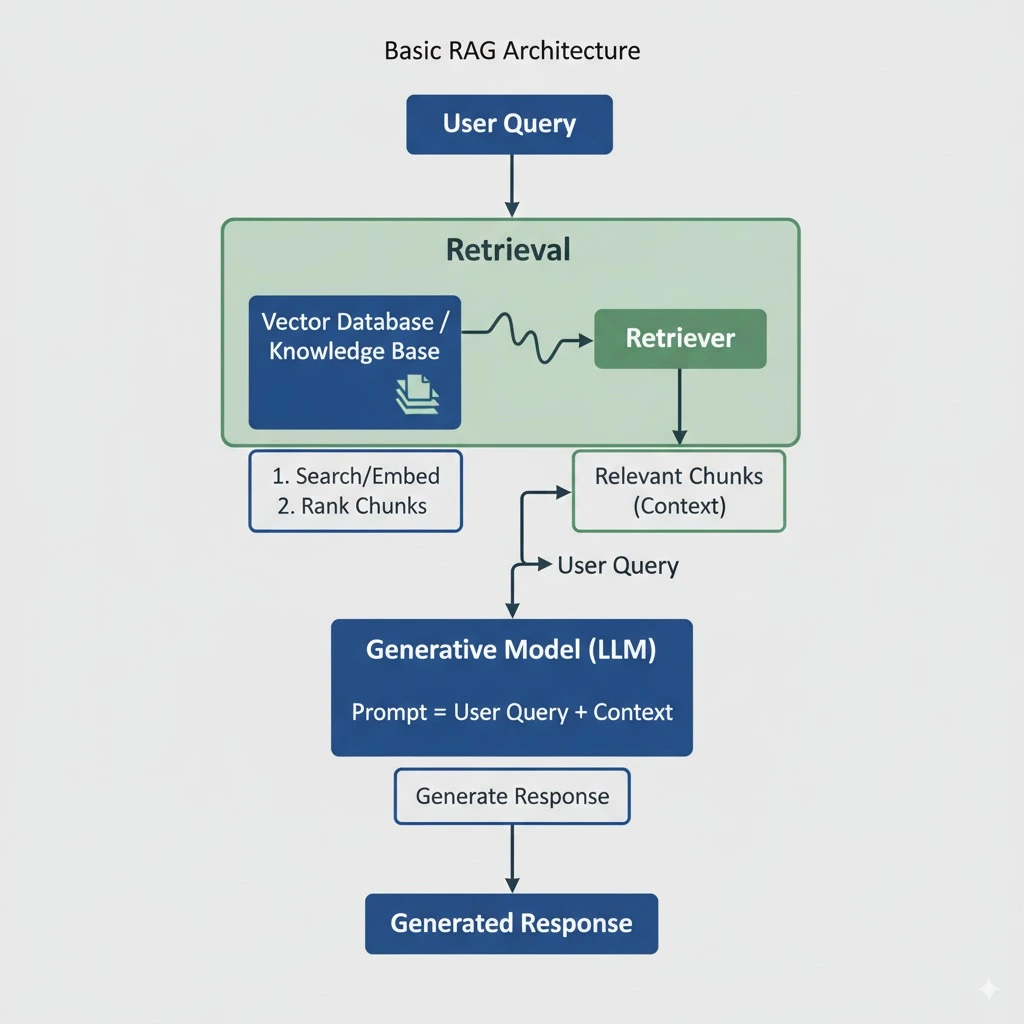 Basic RAG Architecture: Simple but limited approach
Basic RAG Architecture: Simple but limited approach
Here's how basic RAG works:
- User asks a question ("What is AI?")
- System searches documents using vector similarity
- Finds relevant chunks of text
- Generates answer using those chunks
- Returns response to user
It's like having a research assistant who:
- Takes your question
- Looks through documents
- Picks relevant parts
- Writes a summary
The problem? This approach is too simple for complex questions.
The Problems with Basic RAG
Basic RAG works fine for simple questions, but fails when things get complicated:
- Can't handle complex queries: "Compare machine learning vs deep learning for image recognition"
- No query understanding: Treats "What is AI?" and "How does AI work?" the same way
- Poor context quality: Often retrieves irrelevant information
- No source verification: Can't check if retrieved information is actually useful
- Single search strategy: Uses the same approach for all questions
What Makes RAG "Advanced"?
Advanced RAG is like having a smart research team instead of just one assistant. It thinks before it acts, uses multiple strategies, and double-checks its work.
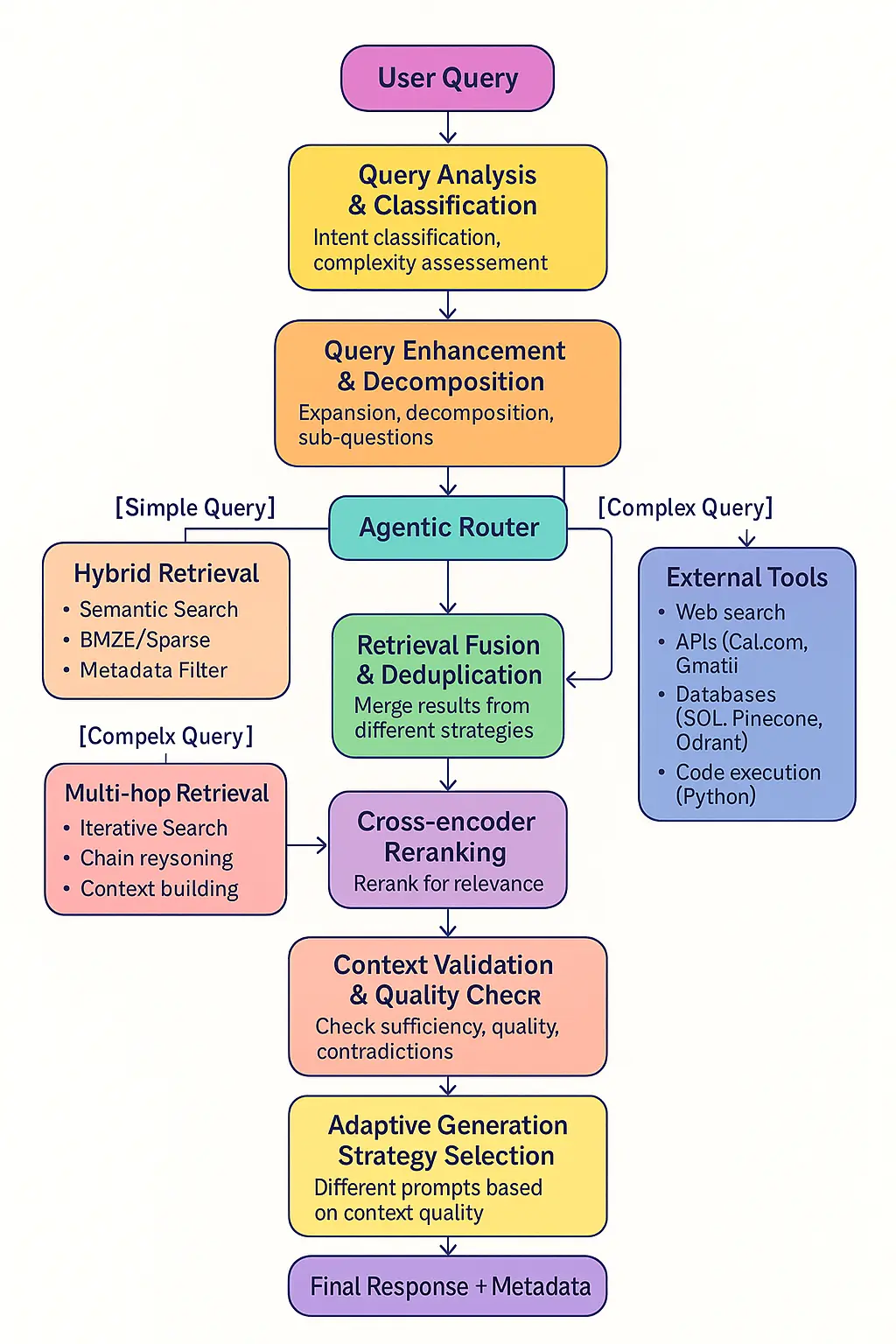 Advanced RAG: A complete intelligent system with multiple components
Advanced RAG: A complete intelligent system with multiple components
Advanced RAG adds:
- Query analysis: Understands what you're really asking
- Smart routing: Uses different strategies for different questions
- Multiple search methods: Hybrid search, multi-hop reasoning
- Quality checking: Validates information before generating answers
- Self-correction: Improves responses based on context quality
Advanced RAG Architecture
Let me break down each component of advanced RAG:
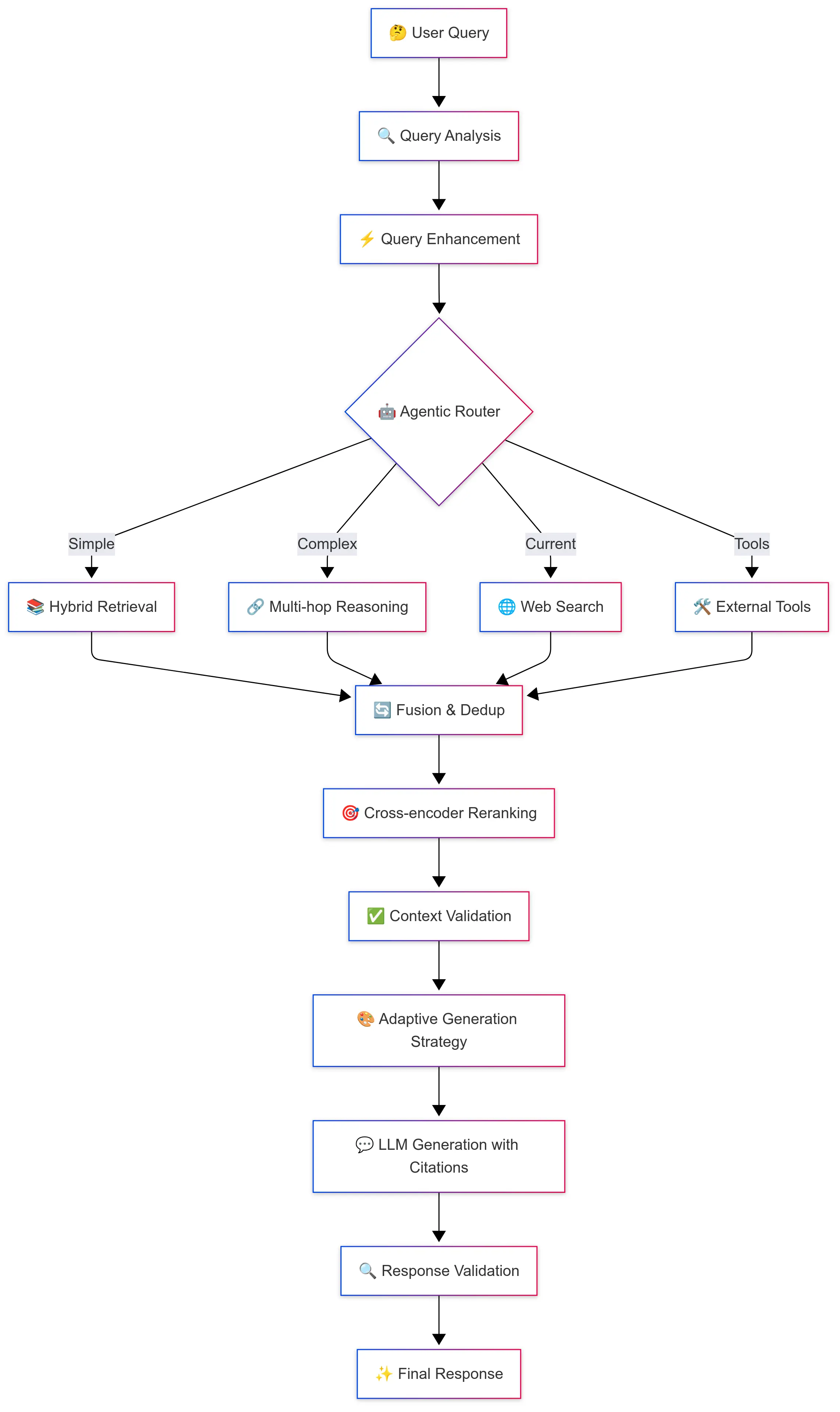 Advanced RAG Flow: From query to final response with quality checks
Advanced RAG Flow: From query to final response with quality checks
Key Components Explained
1. Query Analysis & Classification
Before searching, the system analyzes your question:
- Intent classification: Is this factual, analytical, or comparative?
- Complexity assessment: Simple, moderate, or complex query?
- Entity extraction: What key topics are involved?
Example:
Query: "Compare machine learning and deep learning for images"
Analysis:
- Type: Comparative
- Complexity: Complex
- Entities: [ML, DL, image recognition]2. Query Enhancement & Decomposition
For complex questions, the system breaks them down:
- Original: "Compare ML and DL for images"
- Enhanced sub-questions:
- "What is machine learning for image recognition?"
- "What is deep learning for image recognition?"
- "What are the key differences?"
3. Agentic Router
This is the "brain" that decides which strategy to use:
- Simple queries → Basic hybrid search
- Complex queries → Multi-hop reasoning
- Current events → Web search
- Technical questions → External tools/APIs
4. Multiple Retrieval Strategies
Hybrid Retrieval combines:
- Semantic search: Understands meaning and context
- Keyword search (BM25): Finds exact terms and phrases
- Metadata filtering: Narrows results by type, date, source
Multi-hop Reasoning:
- Searches for each sub-question separately
- Builds context step by step
- Connects related information across searches
5. External Tools Integration
Advanced RAG can use external resources:
- Web search: For current information
- APIs: Calculator, weather, stock prices
- Databases: SQL queries, specialized data sources
- Code execution: For computational tasks
6. Cross-encoder Reranking
After getting search results, the system:
- Re-scores all retrieved documents
- Ranks by true relevance to the specific query
- Filters out low-quality or irrelevant content
7. Context Validation & Quality Check
Before generating the final answer:
- Sufficiency check: Is there enough information?
- Quality assessment: Is the information reliable?
- Contradiction detection: Are there conflicting facts?
8. Adaptive Generation Strategy
Based on context quality, the system chooses:
- High confidence: Detailed answer with citations
- Medium confidence: General answer with caveats
- Low confidence: Request for more specific information
Real-World Example
Let's see advanced RAG in action:
User Query: "How do I reduce my company's carbon footprint while maintaining profitability?"
Step-by-step process:
- Analysis: Complex, analytical query about business and environment
- Enhancement: Breaks into sub-questions about green practices, cost analysis, ROI calculations
- Routing: Uses multi-hop search + external tools for calculations
- Retrieval: Searches for sustainability practices, cost data, case studies
- External tools: Accesses carbon footprint calculators, financial APIs
- Validation: Checks for recent data, verifies cost estimates
- Generation: Creates comprehensive plan with specific recommendations and projected savings
- Response: Detailed action plan with timelines, costs, and expected returns
Result: Instead of generic advice, you get a tailored business plan with real numbers and actionable steps.
Why LangChain, LlamaIndex & LangGraph Are the Best RAG Frameworks in 2025
Building advanced RAG from scratch would take thousands of lines of code. In 2025, LangChain, LlamaIndex, and LangGraph have emerged as the best RAG frameworks for building custom AI solutions. Here's why:
LangChain vs LlamaIndex: When to Use Each
| Framework | Best For | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|
| LangChain | Complex workflows, multi-step chains | Flexibility & ecosystem |
| LlamaIndex | Document-heavy RAG, data indexing | Optimized retrieval |
| LangGraph | Agentic workflows, state machines | Cyclic graphs & routing |
Without These Frameworks (Manual Way):
# 200+ lines of custom code for hybrid search
semantic_results = vector_search(query)
bm25_results = keyword_search(query)
combined = custom_rrf_function(semantic_results, bm25_results)With LangChain:
# 3 lines with built-in optimization
ensemble = EnsembleRetriever(
retrievers=[vector_retriever, bm25_retriever],
weights=[0.6, 0.4]
)
results = ensemble.get_relevant_documents(query)With LlamaIndex:
# Simple document indexing and querying
from llama_index import VectorStoreIndex, SimpleDirectoryReader
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("data").load_data()
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query("Your question here")LangGraph Benefits for Agentic RAG:
- Automatic routing: No complex if-else logic
- State management: Handles data flow between components
- Error handling: Built-in retries and fallbacks
- Tool integration: Easy external API connections
- Cyclic workflows: Perfect for self-correcting RAG systems
Implementation Benefits
Advanced RAG with LangChain/LangGraph provides:
- Better Accuracy: Smart routing and validation reduce wrong answers
- Faster Development: Pre-built components save months of coding
- Easy Scaling: Add new tools and strategies without rewriting code
- Reliable Performance: Built-in error handling and optimization
- Maintainable Code: Clean, structured approach vs spaghetti code
Use Cases for Advanced RAG
Advanced RAG excels in:
- Business Intelligence: Complex analysis requiring multiple data sources
- Research Assistance: Multi-step research with source verification
- Technical Support: Troubleshooting that requires checking logs, APIs, documentation
- Financial Analysis: Combining market data, calculations, and trend analysis
- Healthcare: Medical queries requiring symptom analysis and treatment options
- Education: Personalized learning with adaptive content delivery
Getting Started
To build your own advanced RAG system:
- Start with basic RAG - Get the fundamentals right
- Add query analysis - Use Pydantic models for structured output
- Implement hybrid search - Combine semantic + keyword search
- Add routing logic - Use LangGraph for decision making
- Include external tools - APIs, databases, web search
- Add validation - Quality checks and source verification
- Test and iterate - Continuous improvement based on real usage
Recommended stack for custom AI solutions:
- LangChain: For RAG components, chains, and tool integrations
- LlamaIndex: For document indexing and optimized retrieval
- LangGraph: For agentic workflows, routing, and state management
- Pinecone/Weaviate/Qdrant: For vector storage
- OpenAI/Anthropic/Google: For LLM inference
- Pydantic: For structured outputs
Conclusion
Advanced RAG represents the next evolution of AI information systems. While basic RAG is like having a simple search tool, advanced RAG is like having an intelligent research team that understands your needs, uses the right strategies, and delivers high-quality results.
The key difference is intelligence at every step: from understanding queries to validating results. With tools like LangChain and LangGraph, building these sophisticated systems is now accessible to developers without requiring months of custom development.
As AI continues to evolve, advanced RAG techniques will become the standard for any serious information retrieval system. The investment in learning and implementing these techniques will pay off in better user experiences, more accurate results, and systems that can handle the complexity of real-world information needs.
Ready to upgrade your RAG system? Start with query analysis and hybrid search - you'll immediately see the difference in response quality.
Want to see advanced RAG in action? Check out my portfolio for live demos and implementation examples.
Need Help Implementing AI Solutions?
I specialize in RAG systems, AI agents, and custom integrations. Let's build something extraordinary.
Get Expert Consultation
